Share this
Selecting the Right Grab Sampling Equipment for a Northern California Plant
by Morgan Zealear on 7/29/21 12:00 PM

Grab sampling—also known as spot sampling, laboratory sampling, field sampling, and closed-loop sampling—involves the manual collection of a sample of fluid in a pipeline, tank, or system and its transportation to a laboratory for qualitative analysis. The right grab sampling equipment can obtain representative fluid samples to verify and confirm several aspects of processes for Northern California plants.
To obtain a meaningful and representative sample depends highly on the equipment selected, panel design, and proper collection of the fluid. Below we detail the basics of grab sampling and best practices for equipment design, cylinder selection, and sample collection.
| Click to Watch How to Develop the Right Grab Sampling System for your Plant |
Grab Sampling Basics
While there are many different styles of grab sampling systems, we categorize them into two categories:
- Cylinder panels for sampling gases and volatile liquid
- Bottle panels for sampling non-volatile liquids
Grab sampling is often a critical function for Northern California plants and can be used for sampling storage tanks, long transport lines, process lines, flare emissions, and process analyzers for:
- Validation of process conditions
- Validation that end products meeting quality specifications
- Confirmation of product quality during custody transfers
- Validation of online analyzers
- Evaluation of environmental emissions
- Measurement of raw components such as crude
Pros and Cons of Grab Sampling Compared to Online Analyzers
Grab sampling and online analyzers both have their advantages and disadvantages depending on the application, process conditions, and time constraints. Let’s take a look into the pros and cons of grab sampling as it compares to online analyzers.
Grab Sampling Advantages:
- Less expensive
- Easier installation and maintenance
- Can be installed closer to the process
- Allows analytical expertise to be concentrated in the laboratory
Grab Sampling Disadvantages:
- Time delay
- Harder to maintain the sample at process conditions
- Potentially more dangerous
- Compromised sample purity if the container is not properly cleaned
Grab Sampling Equipment: Best Practices
When designing grab sampling equipment, there are a number of things to keep in mind. Detailed below are general guidelines for grab sampling, design considerations, sample container selection, and best practices for sample collection.
General Rules of Grab Sampling
When sampling from a pipeline, it is important to ensure that the sample is representative, meaning it actually reflects the characteristics of the process. This can be achieved by avoiding phase changes in the sampling system and during transport as well as using probes to sample the center third of the pipe vs. the wall of the pipe.
While grab sampling is inherently not as timely as an online analyzer installation, timeliness is still important. Transport time from the process to the panel and sampling container should be minimized. The time from process to the panel can determine what process corrections should be made based on the results.
A sample can be representative, but may be in the wrong state and thus cannot be injected into the analyzer. Conversely, the sample may be old and non-representative of the process flow due to dead leg contamination, but in the correct state for analysis. It may provide results that may be interpreted as accurate, but they aren’t.
Grab Sampling System Design Considerations
Flush time is the amount of time required to flush out old fluid from supply lines to allow a fresh sample to be captured in the sample container. It is a measure of time required to move the sample from the sample tap to the container and is a function of flow rate and system volume. Utilizing panels with a continuous flow, the transportation line to the sample panel is always flowing and is returned to the process, yielding two significant benefits:
- Reduced flush time to zero: The panel will always contain a fresh sample, as the lines are always flowing.
- No need to dispose of flush fluid: The flow is returned to the process.
It should be noted that flushing and continuous flow are different from purging. Purging utilizes a secondary fluid, typically nitrogen, to flow through the panel for cleaning purposes. Purging is often done when a sample is toxic or a sample is a warm liquid that may cool and solidify, clogging the lines.
Sample Behavior and Container Selection
It is critical to prevent volatile liquids from vaporizing, due to fractionation. Similarly, it is important to prevent condensation in gas samples. Thus,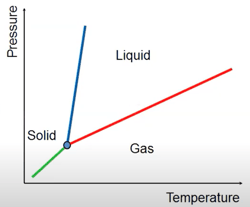 it is important to understand changes in pressure and temperature, as such changes can affect the sample. As temperature increases (or pressure decreases), lighter components can vaporize out of liquid samples before heavier components. In parallel, as temperature decreases (or pressure increases), heavier components will condense out of gas samples before lighter components. Thus, avoiding phase changes and maintaining the sample at process conditions are crucial to maintaining the composition of the sample.
it is important to understand changes in pressure and temperature, as such changes can affect the sample. As temperature increases (or pressure decreases), lighter components can vaporize out of liquid samples before heavier components. In parallel, as temperature decreases (or pressure increases), heavier components will condense out of gas samples before lighter components. Thus, avoiding phase changes and maintaining the sample at process conditions are crucial to maintaining the composition of the sample.
Sample container selection depends heavily on sample toxicity, budget, sample pressure, and sample volatility. Sample cylinders are more suitable for gases, toxic samples, or samples which must be maintained at a specific pressure to maintain process conditions. Bottles are more suitable for nonvolatile liquids. The matrix below shows general guidelines for selecting a sample container.
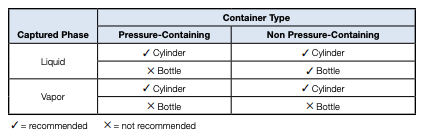
Best Practices for Sample Collection
When using sample cylinders for grab sampling, there are a few basic rules to follow in addition to proper sampling procedures:
- Filling the cylinder in a vertical orientation
- Filling liquids from the bottom of the cylinder
- Filling gases from the top of the cylinder
Similarly, when using bottles for grab sampling, best practices include:
- Using needles and septum
- Using a shroud to guide bottle into needles
With sample cylinders, there is always a concern with the over-pressurization of the container. For liquid samples, an outage tube is often used to create a vapor space, thus protecting the cylinder from over-pressurization due to thermal expansion of the liquid. For either gases or liquids, rupture discs and relief valves are typically used to prevent over-pressurization. However, it should be noted that rupture discs and relief valves should not be used for sampling applications involving a toxic fluid.
Look to Grab Sampling Equipment Experts at Swagelok Northern California
Whether you need to install a new custom-configured grab sampling system—or optimize your current system to better inform the process—Swagelok Northern California has you covered. With our proven industry expertise, superior component quality, and industry-leading assembly services, we are your top choice for grab sampling equipment. To learn more about our custom configurable grab sampling panels and sample cylinders, contact our team or download our presentation and watch the webinar replay below.
Download the Presentation and Watch the Webinar Replay
To find out more about how Swagelok Northern California can help you select the right grab sampling equipment for Northern California plants, contact our team today by calling 510-933-6200.
 Morgan Zealear | Product Engineer – Assembly Services
Morgan Zealear | Product Engineer – Assembly Services
Morgan holds a B.S. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of California at Santa Barbara. He is certified in Section IX, Grab Sample Panel Configuration, and Mechanical Efficiency Program Specification (API 682). He is also well-versed in B31.3 Process Piping Code. Before joining Swagelok Northern California, he was a Manufacturing Engineer at Sierra Instruments, primarily focused on capillary thermal meters for the semiconductor industry (ASML).
Share this
- Archive (465)
- Assembly Services (207)
- About (100)
- Seal Support Systems (96)
- Best Practices (88)
- Training Services (74)
- Fittings (51)
- Semiconductor Applications (49)
- Hoses and Flexible Tubing (47)
- Regulators (44)
- Tubing (42)
- Grab Sampling Systems (32)
- Sampling Systems (32)
- Gas Systems (30)
- Services (30)
- Downloads (29)
- Valves (24)
- Application Support (18)
- Orbital Welding (17)
- Case Studies (13)
- Steam Systems (13)
- Frequently Asked Questions (12)
- Tools (12)
- Measurement Devices (7)
- Subsystems (6)
- Thermal Management (6)
- September 2023 (1)
- August 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (1)
- March 2023 (3)
- February 2023 (3)
- January 2023 (4)
- December 2022 (4)
- November 2022 (4)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (1)
- August 2022 (3)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (4)
- May 2022 (1)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (1)
- November 2021 (6)
- October 2021 (6)
- September 2021 (8)
- August 2021 (4)
- July 2021 (3)
- June 2021 (6)
- May 2021 (6)
- April 2021 (7)
- March 2021 (5)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (6)
- December 2020 (5)
- November 2020 (6)
- October 2020 (6)
- September 2020 (8)
- August 2020 (7)
- July 2020 (8)
- June 2020 (8)
- May 2020 (6)
- April 2020 (9)
- March 2020 (7)
- February 2020 (10)
- January 2020 (21)
- December 2019 (23)
- November 2019 (21)
- October 2019 (22)
- September 2019 (21)
- August 2019 (22)
- July 2019 (23)
- June 2019 (20)
- May 2019 (23)
- April 2019 (22)
- March 2019 (21)
- February 2019 (20)
- January 2019 (21)
- December 2018 (14)
- November 2018 (19)
- October 2018 (23)
- September 2018 (17)
- August 2018 (29)
- July 2018 (11)
- June 2018 (6)
- May 2018 (5)
- April 2018 (4)
- March 2018 (5)
- February 2018 (3)
- January 2018 (3)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (4)
- October 2017 (3)
- September 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (6)
- July 2017 (4)
- June 2017 (4)
- May 2017 (4)
- April 2017 (3)
- March 2017 (4)
- February 2017 (3)
- January 2017 (3)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (3)
- October 2016 (3)
- September 2016 (5)
- August 2016 (5)
- July 2016 (4)
- June 2016 (5)
- May 2016 (3)
- April 2016 (4)
- March 2016 (5)
- February 2016 (11)
- January 2016 (1)
- December 2015 (3)
- November 2015 (4)
- October 2015 (3)
- September 2015 (4)
- August 2015 (4)
- July 2015 (8)
- June 2015 (5)
- May 2015 (3)
- April 2015 (4)
- March 2015 (4)
- February 2015 (3)
- January 2015 (4)
- December 2014 (2)
- November 2014 (3)
- October 2014 (4)
- September 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (4)
- July 2014 (5)
- June 2014 (4)
- May 2014 (4)
- April 2014 (5)
- March 2014 (4)
- February 2014 (3)
- January 2014 (4)
- December 2013 (5)
- November 2013 (3)
- October 2013 (4)
- September 2013 (3)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (5)
- June 2013 (5)
- May 2013 (3)
- April 2013 (6)
- March 2013 (4)
- February 2013 (4)
- January 2013 (8)
- December 2012 (4)
- November 2012 (6)
- October 2012 (6)
- September 2012 (4)
- August 2012 (4)
- July 2012 (4)
- June 2012 (4)

.webp?width=210&height=70&name=StickyLogo%20(5).webp)